4 C’s of Diamonds: Diamond Guide

Listen to our podcast episode: The Ins and Outs of Natural Diamonds.
John Atencio Diamonds
Diamonds sourced by John Atencio reflect a commitment to excellence and integrity. His reputation reflects 48 years of building long-standing relationships with miners, cutters, and diamond suppliers – while maintaining a steadfast dedication to ethical and sustainable diamond sourcing. This commitment gives the John Atencio customer confidence that the diamond they buy will be free from the taint of war or human suffering.
As with any diamond, the 4Cs — Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight play an integral part in gauging value and rarity. At John Atencio, our Diamond Experts work to ensure that our customer’s requirements in terms of size, clarity, cut, and color are met while maintaining the highest standards.

What Are the 4 C's of Diamonds?
Since every diamond is unique, each has certain distinguishing characteristics. The 4Cs are a globally accepted standard for assessing the quality of a diamond.

Diamond Cut
The most important of the 4Cs is Diamond Cut. The cut of a diamond determines the symmetry, proportion, and polish of the stone and ultimately indicates how well the diamond’s facets interact with light for maximum sparkle. If a diamond is poorly cut, it will appear dull, even with a high clarity and color. More than any other factor, the cut determines the beauty of the stone.
The diamond cut takes into account the design and craftsmanship of the diamond, including its weight relative to the diameter, girdle thickness, the symmetry of its facets, and the quality of the polish on those facets.
Precise artistry and workmanship of the cutter is required to fashion a stone so it delivers a magnificent return of light. The visual effects that are considered desirable include the following:
Brightness: Internal and external white light reflected from a diamond
Fire: The scattering of white light into all the colors of the rainbow
Scintillation: The amount of sparkle a diamond produces and the pattern of light and dark areas caused by reflections within the diamond.
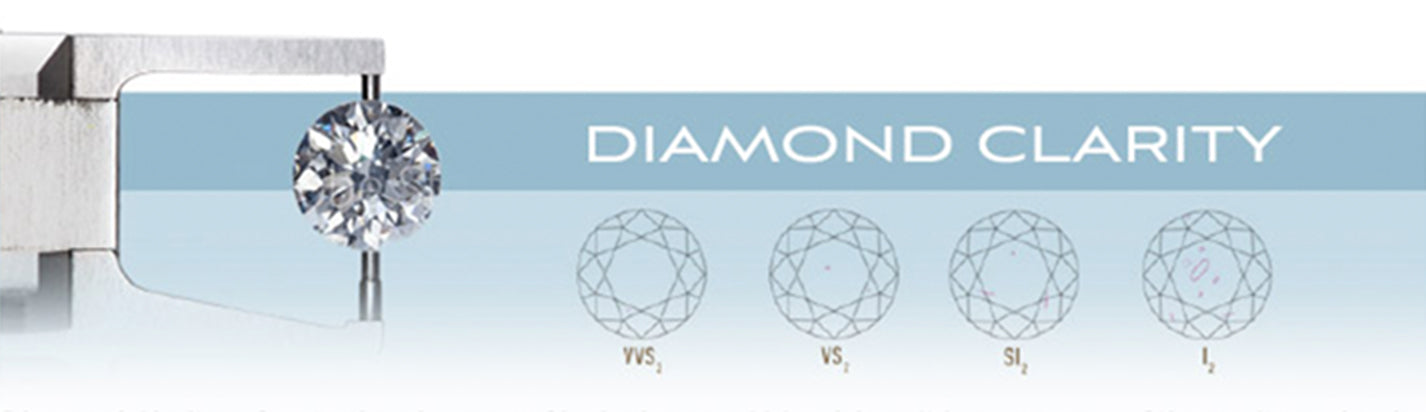
Diamond Clarity
Diamond Clarity refers to the absence of inclusions and blemishes. It is a measure of the purity and rarity of a stone, as graded under 10x magnification. A stone is considered flawless if, under magnification, it shows no inclusions (internal flaws) and no blemishes (external imperfections).
To fully understand diamond clarity, you need to understand how natural (mined) diamonds are created. Natural diamonds are the result of carbon exposed to extreme heat and pressure deep in the earth. This process naturally results in a variety of internal and external imperfections.
Beyond flawless diamonds, evaluating diamond clarity involves determining the number, size, and position of these characteristics, as well as the overall appearance of the stone. The closer a diamond comes to purity, the better its clarity.
Many inclusions are too tiny to be seen with the naked eye and need to be examined by an expert under 10x magnification. To the naked eye, a VS1 and an S12 diamond may look exactly the same, but these diamonds are quite different in terms of overall quality. This is why an expert and accurate assessment of diamond clarity by a John Atencio consultant is extremely important.
The Diamond Clarity Chart has 6 categories. Some are divided for a total of 11 specific grades.
Flawless (FL) - No inclusions and no blemishes visible under 10X magnification
Internally Flawless (IF) - No inclusions visible under 10X magnification
Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) - Inclusions are observed under 10X magnification and are characterized as minor.
Slightly Included (S11 and S12) - Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification.
Included (I1, I2, and I3) - Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification and may be visible to the naked eye.

Carat Weight
A Diamond’s carat weight measures how much a diamond weighs.
A metric ‘carat’ is defined as 200 milligrams. Each carat is divided into 100 ‘points’. This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place.
The carat weight of a diamond can appear differently based on the shape of the diamond – such as round brilliant, pear, oval, cushion, marquise, emerald, or radiant. It is important to note that carat weight does not necessarily correlate with size. Two diamonds might have the same carat weight but appear quite different due to their proportions.
Everything else being equal, the diamond price increases with the carat weight because larger diamonds are rarer and generally more desirable. Importantly, the other factors of Color, Clarity and Cut also have an impact on value.

Diamond Color
Diamond color means the absence of color and refers to the natural tint of a diamond. The closer it is to being truly ‘colorless, the rarer it is. From colorless, it moves to warm whites with hints of yellow.
After which they become Fancy colors. Many diamond color distinctions are so subtle that they are invisible to the untrained eye. However, color distinctions make a big difference in diamond quality and price.
When assessing the color of a diamond, there are several factors to consider. The most crucial aspect is the stone's hue, followed by its tone, which refers to how light or dark the color appears, and saturation, or how intense the color is. While these factors are significant, remember that they do not function independently.
For instance, a diamond with a light tone might still exhibit a rich color if it has high saturation. Another critical aspect is the overall uniformity of the diamond's color, which is evaluated by looking at the stone from various angles and under different light conditions. The diamond's size also impacts color perception; larger diamonds tend to show more color.
The color grade of a diamond significantly affects its value. A colorless diamond, graded D, is the most sought-after, as it's the rarest. Diamonds graded E or F are considered colorless, too, but with minute traces of color that can only be detected by gemologists.
As you move down the grading scale from G to J, diamonds are nearly colorless, and the color is difficult to detect unless compared side by side with diamonds of a higher grade. Beyond this, diamonds from K to Z show a faint to light color, which might be visible to the naked eye and may reduce the value of the stone.
However, after Z, diamonds enter the 'Fancy' category and are assessed differently. In this category, the more color a diamond has, the more valuable it becomes. These fancy color diamonds are rare and come in blues, greens, yellows, oranges, pinks, and reds, among other hues.
The importance of color in diamond selection can be influenced by a variety of factors. Firstly, individual preference plays a significant role. Some people prefer the pure, icy brilliance of a colorless diamond, while others may be drawn to the warmth of a slightly colored diamond or even the vibrancy of a fancy-colored diamond.
The setting of the diamond can also affect the importance of color. For example, in yellow or rose gold settings, diamonds with a faint yellow hue can appear more colorless, and the overall effect can be quite beautiful.
Lastly, the diamond's shape and cut can affect color perception. Certain cuts, like round or princess, may conceal color better than others, like emerald or pear, which tend to reveal more color. This consideration may lead buyers to opt for higher color grades in certain cuts. Similarly, color may be more apparent in larger diamonds, influencing a buyer to prioritize color in larger-carat stones.
Which Features Matter Most?
In the diamond buying world, it's essential to know about the 4 C’s. But knowing what they are is just the first step. Now, we need to dig a little deeper and understand the significance of each of these factors and their role in determining a diamond's value and beauty.
Carat Weight: Beauty and Value
Carat weight is often the most straightforward of the 4 Cs. It directly impacts a diamond's size, which is undoubtedly an eye-catching factor. A bigger diamond is easy to notice and can convey a sense of luxury and prestige. It also greatly affects the diamond's price, as larger diamonds are rarer and therefore more expensive.
However, bigger is not always better. A large diamond with poor cut, color, or clarity may not be as appealing or valuable as a smaller one with superior quality in these aspects. Thus, while carat weight contributes significantly to a diamond's beauty and value, it needs to be balanced with the other 3 Cs for the best outcome.
Cut: The Artistry Behind the Brilliance
When we talk about a diamond's cut, we're discussing the human contribution to a diamond's beauty. The precision, symmetry, and polish of the facets can dramatically influence how light interacts with the diamond, affecting its brilliance and fire.
Even a high-carat diamond with exceptional color and clarity can appear dull and lifeless if it's poorly cut. Conversely, a masterfully cut diamond can maximize light return, making a stone of lower clarity or color grade appear more stunning. Hence, the cut should never be overlooked. It can compensate for other Cs to a certain degree, but a poor cut can also undermine the diamond's potential beauty and value.
Color: The Subtle Shades of Value
As previously mentioned, in most cases, the less color, the higher the grade and the value. Color can subtly impact a diamond's appearance, especially in contrast with the setting.
Though some color differences can be hard to detect with an untrained eye, they do contribute to the overall quality and price of a diamond. However, if the diamond is brilliantly cut, it can often mask some color, reflecting light in a way that minimizes the appearance of yellow hues. Therefore, color should be considered in balance with the other Cs, particularly the cut.
Clarity: The Hidden Intricacies
Diamond clarity refers to the presence of internal or external flaws, known as inclusions and blemishes. Flawless diamonds are rare and highly prized, contributing to their value.
However, many inclusions and blemishes are microscopic and do not affect a diamond's beauty to the naked eye. In this case, a diamond with lower clarity but excellent cut and color can still look stunning. As such, while clarity is important, it is often considered less critical than cut and can be balanced against the other Cs depending on your personal preference and budget.
Ultimately, the 4 Cs should not be viewed in isolation. Instead, consider them as parts of a whole, each contributing to the overall beauty and value of a diamond in its own way. Your perfect diamond might not be the one that scores the highest in each category, but the one that balances these four factors in a way that is most pleasing to you.
Getting Expert Guidance
At John Atencio, when we say “perfect,” we mean the perfect diamond for you. This means the diamond has the characteristics you desire and is within your budget. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to choosing the perfect diamond for your engagement ring.
As a general recommendation, it's best to ask for assistance from an expert. This is the best way to ensure that you won’t end up paying for a feature that will go unnoticed or purchasing a diamond that will distract or interfere with light reflection.
While choosing the right diamond can be intimidating, your experience needn’t feel that way. At John Atencio, our Diamond Experts can show you how to pick a diamond for your bride-to-be. Our thoughtful team always works to ensure that we meet our customer’s needs in terms of size, clarity, cut, and color, all while maintaining the highest standards.
Use our helpful diamond search and then make an appointment at one of our locations, where our attentive, knowledgeable experts can guide you toward the perfect ring for your unique love story.


